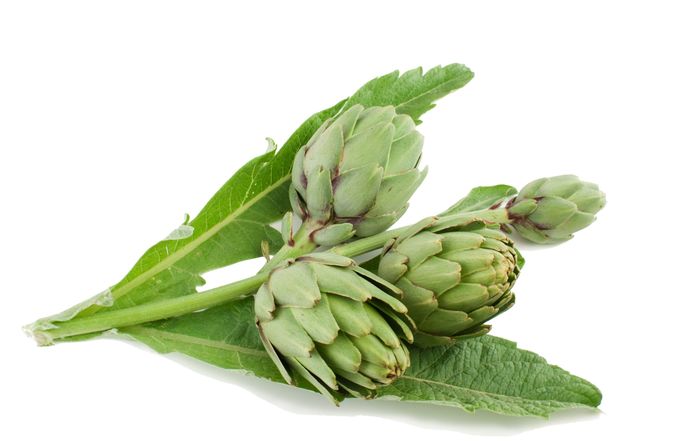
Artichoke
Cynarascolymus, the artichoke is a herbaceous plant from Cynara genre of the Asteraceae family. It is grown since ancient times as food in mild climate.
The artichoke season goes from autumn to spring.
The highest quality artichokes are the heaviest ones in relation with its size and its leaves well tight; if we press the artichoke next to our ear and we hear a crack that means it is still fresh.
It is sold fresh, frozen and canned, whole or chopped.
After water, its main compound are carbohydrates (2.90 grams per 100 grams of artichoke), among which it is prominent inulin and fibre. Inulin is the predominant carbohydrate. This substance is metabolised in the organism and results in fructose units, a sugar that does not need insulin, that is why artichokes are part of the diabetics diet.
As they are rich in fibre they provide the feeling of satiety and favorise the intestinal transit, so it contributes to relieve or prevent constipation.
The main minerals are sodium, potassium, phosphorous and calcium and among vitamins there are B1, B3 and small quantities of vitamin C. Nonetheless, what is important of its composition are other substances that although they appear in small quantities they have physiological benefits:
Cynarine is an acid substance with a choleretic and diuretic effect. Furthermore it avoids the endogenous synthesis of cholesterol and other lipids, and at the same time it increases biliary cholesterol excretion.
Sterols limit the cholesterol absorption in the intestine
Due to the important fibre quantity that it contains, it is flatulent for lots of people who tend to suffer heavy digestions and accumulate gasses.
-
Type of dish
- Beers
- Cocktails
- Breakfasts and brunch
- Burguers
- Juices, milkshakes and beverages
- Shellfish
- Bread and pastries
- Pizzas, patty
- Dessert
- Pasta
- Sándwich
- Pastries
- Finger foods
- Ice creams and sorbets
- Legumes
- Salads
- Eggs
- Patty
- liqueur
- Harvard plate
- Main course
- Meats
- Fish
- Birds
- Vegetables
- Soups and creams
- Rices
- Coffee, chocolate and infusion
- Cheeses
- Appetizers and canapes
- Temperature
- Cuisine type
- Additional culinary preparation
- Conservation technique
- Seasonal recipes
-
- Aromatic herbs
- Beverages
- Big game hunt
- Bread and pastries
- Canned goods and pickles
- Cereals
- Condiments, spices and additives
- Cooked, salted, preserved and cold meats
- Dried fruits and nuts
- Dry pulses
- Edible oils and vinegars
- Eggs and derivatives
- Feathered game hunt
- Fish cuts
- Fishes
- Insects
- Kitchen and bakery tecniques
- Kitchen and bakery utensils
- Meat cuts
- Meats
- Milk, cream and derivatives
- Mushrooms
- Offal
- Pasta, rice, flour and derivatives
- Poultry
- Seafood
- Service techniques
- Service utensils
- Vegetables cuts
- Vegetables, fruits, tubers and seaweed