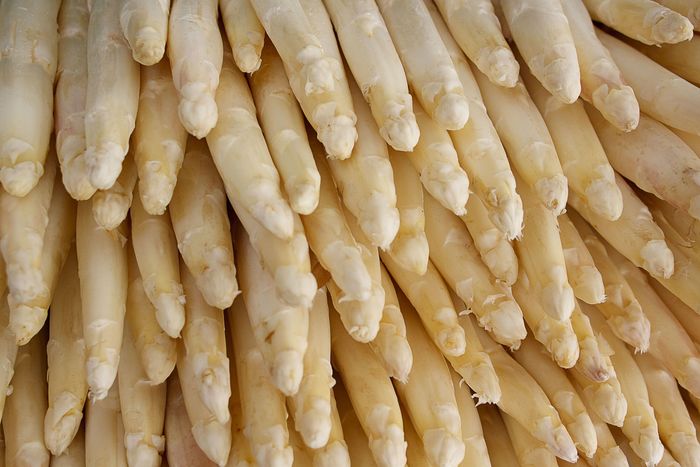
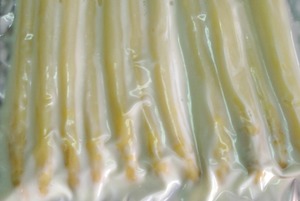
White asparagus
Asparagus are the young tender stems from the asparagus plant, an herbaceous plant from the Liliaceous family that reaches up to a meter and a half of height. Other vegetables such as onions and leeks belong to this family. However, asparagus don’t look like them nor they taste the same. Many of the plants in this family belong to different genus, they form bulbs and they are all rich in saturated volatile essential oils which are beneficial for our health.
White asparagus are obtained by avoiding the exposure to sunlight while they grow.
Thanks to greenhouses, we can buy asparagus all year round, although their best consumption time goes from April to May., The agro-food industry also works in the production of canned asparagus, which are in high demand in all countries.
When we buy fresh asparagus we must pick the ones with closed and compact edges, firm and straight stems and without colour variations. We should avoid those with hits or stains. Anyways it is recommended not to buy asparagus with dirt on their scales because they’d be hard to clean and their washing would cause a loss of nutrients. Thin asparagus aren’t better than thick ones; both have an exquisite taste.
To be able to preserve fresh asparagus properly and maintain their quality, they must be wrapped around a moist cloth and leave them in the fridge for up to three weeks. If they are put in a plastic bag they only last for about 2 or 3 days. They get harder as time goes by, so they should be consumed as soon as possible.
Asparagus can be frozen but they are not as firm when unfrozen.
-
Type of dish
- Beers
- Cocktails
- Breakfasts and brunch
- Burguers
- Juices, milkshakes and beverages
- Shellfish
- Bread and pastries
- Pizzas, patty
- Dessert
- Pasta
- Sándwich
- Pastries
- Finger foods
- Ice creams and sorbets
- Legumes
- Salads
- Eggs
- Patty
- liqueur
- Harvard plate
- Main course
- Meats
- Fish
- Birds
- Vegetables
- Soups and creams
- Rices
- Coffee, chocolate and infusion
- Cheeses
- Appetizers and canapes
- Temperature
- Cuisine type
- Additional culinary preparation
- Conservation technique
- Seasonal recipes
-
- Aromatic herbs
- Beverages
- Big game hunt
- Bread and pastries
- Canned goods and pickles
- Cereals
- Condiments, spices and additives
- Cooked, salted, preserved and cold meats
- Dried fruits and nuts
- Dry pulses
- Edible oils and vinegars
- Eggs and derivatives
- Feathered game hunt
- Fish cuts
- Fishes
- Insects
- Kitchen and bakery tecniques
- Kitchen and bakery utensils
- Meat cuts
- Meats
- Milk, cream and derivatives
- Mushrooms
- Offal
- Pasta, rice, flour and derivatives
- Poultry
- Seafood
- Service techniques
- Service utensils
- Vegetables cuts
- Vegetables, fruits, tubers and seaweed